Control Based on Priority Pest
go.ncsu.edu/readext?297853
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲Pest Control Based on Most Problem Pest
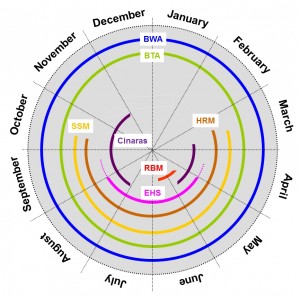 Click on graphic for larger image.
Click on graphic for larger image.
Printer friendly PDF
Growers have multiple pests that need to be controlled. Deciding when to treat and with what gets complicated. The pest control color wheel illustrates the various treatment windows for the different pests. Some pests, like the rosette bud mite (RBM), have a very narrow window for control. Therefore, it is the first pest to consider. If you have RBM, read through “Focus on rosette bud mite control” first. Control of virtually all other pests except for fall treatment of Cinara aphids can occur during the treatment window for RBM.
If you don’t have RBM, the second pest to consider is elongate hemlock scale (EHS). For treatment options for EHS control plus all other pests, see “Focus on elongate hemlock scale control.” Again, you can control all pests while controlling EHS.
The third pest to consider is balsam woolly adelgid (BWA). These can be controlled virtually any time of year.
If you don’t have RBM, EHS or BWA but are nearing harvest, then control of Cinara and twig aphids because most important.
Mite control can be added on any time other pests are being controlled except during the winter months. The focus on mite control page has information on miticides and when they should be added.

- Focus on rosette bud mite control — If rosette bud mites are your problem, look no further for the control of all pests except Cinara aphids in market size trees.
- Focus on elongate hemlock scale control — If you don’t have rosette bud mites but do have elongate hemlock scale, look here for control of all your pests.
- Focus on balsam woolly adelgid control — No rosette buds or scales but you do have woollies? Look here for control.
- Focus on aphid control — Nearing harvest? RBM, EHS and BWA not a problem? Then the balsam twig aphid and Cinara aphids are your number one concern.
- Focus on mite control — Mite control can be added on any time other pests are being controlled. Look here for added information on mite control.


